
CLEAN WATER AND SANITATION
In our interconnected world, the battle for clean water and proper sanitation has never been more crucial. As a beacon of hope in the United Nations' 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6) champions the universal right to safe water and effective sanitation, essential for thriving communities and a healthy planet. This report delves into Nitte (Deemed to be University)'s innovative and impactful efforts to achieve SDG 6, highlighting pioneering strategies, active community engagement, and sustainable practices that have transformed water management and fostered a culture of environmental stewardship both within and beyond its campuses.

Proactive steps taken by NU Ensuring access to adequate and equitable sanitation and hygiene:
Nitte (Deemed to be University) recognizes that promoting public health through disease prevention is paramount for community well-being. Central to this commitment is the establishment of waste water treatment plants and maintenance of proper sanitation facilities such as toilets, and hand washing stations equipped with WHO-recommended steps across all its campuses, catering to diverse needs including those of people with disabilities, the elderly, and children. The university has implemented robust policies that prioritize sanitation and hygiene, reflecting its dedication to ensuring access to clean and safe facilities for all. Substantial budget allocations and ample resources are dedicated to developing and maintaining sanitation infrastructure and associated programs, ensuring comprehensive support for these essential initiatives.

Wastewater Treatment and Reuse Policy:
The policy developed is intended to treat wastewater as an economic resource. The university uses approximately 7.3 lakh liters of water daily, recycling around 6 lakh liters of wastewater daily for non-potable purposes like toilet flushing, irrigation, and vehicle washing. Furthermore, advanced technological units are employed to ensure efficient wastewater treatment, chosen for their operational ease, cost efficiency, and environmental sustainability, aiming to achieve zero wastewater discharge.
Infrastructure for Waste water Management and Hygiene Facilities:
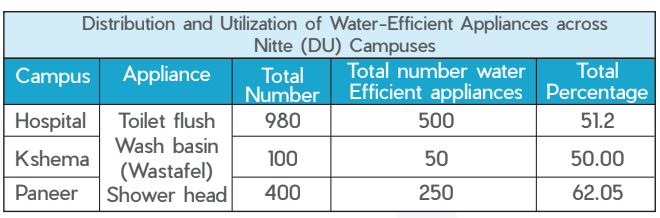
The university operates three STPs with a total capacity of 1450 KLD (800 KLD at JKSH Hospital campus, 400 KLD at KSHEMA campus, and 250 KLD at Paneer campus), Recycled water from these plants is used for gardening and toilet flushing. Rainwater from rooftops is collected via separate pipelines, storing it in raw water storage tanks, and treating it in wastewater treatment plants equipped with pressure sand filters and chlorination units for domestic use. The terrain of the university is contoured to facilitate natural water flow, with Stormwater collected at the lowest points on campus.
Recycled water usage:
Recycled water is used for supporting green landscapes year-round, reducing reliance on freshwater sources. Grey water is recycled and reused for gardening, washing vehicles, and flush water in all campus toilets.

Stormwater Drainage System:
Rainwater from rooftops is collected via separate pipelines, storing it in raw water storage tanks, and treating it in wastewater treatment plants equipped with pressure sand filters and chlorination units for domestic use. The terrain of the university is contoured to ease natural water flow, with Stormwater collected at the lowest points on campus.
Improving water safety and quality:
Students, employees, and visitors to the constituent units, sections, and centers of Nitte (DU) have free access to clean drinking water through UV-based water purifier dispensers. The quality of water is assessed periodically through both in-house and external testing. Major buildings have separate storage facilities for potable and non-potable water, with segregated storage tanks and pipelines for potable water, stormwater, and grey water.


Ensuring sustainable withdrawal and supply of fresh water:
Nitte (DU) prioritizes effective rainwater harvesting as part of its sustainable water management strategy. Systems are installed on all three campuses to manage and use rainwater efficiently. Rainwater from rooftops is collected via separate pipelines and directed into raw water storage tanks, undergoing treatment at a dedicated Water Treatment Plant (WTP). The treated rainwater is used for all domestic purposes within the campus, ensuring sustainable water use practices. Nitte (DU) has implemented separate Stormwater drains to prevent flooding and improve water use, ensuring efficient collection and management of rainwater resources across campuses. Additionally, Nitte (Deemed to be University) extends its rainwater harvesting initiatives beyond campus borders by sourcing rainwater from an off campus, artificially created harvesting pond via a dedicated pipeline. This effort not only supplements the univers it y 's water resources but also p r o m o t e s a n d supports rain water s t o r a g e w i t h i n t h e s u r r o u n d i n g community.

Promotion of off-campus rainwater harvesting:
Nitte (DU) promotes rainwater harvesting off-campus by purchasing rainwater via a dedicated pipeline from an artificial pond near the campus, supporting local rainwater storage and contributing to sustainable water management practices beyond university grounds.
'Every drop counts' campaign:
The Green Brigadiers on campus have launched the 'Every Drop Counts' campaign to emphasize the importance of water conservation, raising awareness and promoting judicious water usage among students and staff. In all departments and streams of Nitte University, drinking water outlets feature educational displays promoting responsible water usage, serving as gentle reminders for the campus community to use water wisely

Improving Water Safety and Quality:
All students, employees, and visitors to the constituent units, sections, and centers of Nitte (DU) have free access to clean drinking water through UV-based water purifier dispensers. The quality of water is assessed periodically through both in-house and external testing. Major buildings have separate storage facilities for potable and non-potable water, with segregated storage tanks and pipelines for potable water, stormwater, and grey water.
Awareness through social media:
Nitte University social media platform create awareness among stake holders about water usage and conservation through the post on world water day.
Integration in curriculum and research:
Nitte (DU) also incorporates Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6) principles into various educational programs to foster a deep u nde r s t a ndi ng of wate r conservation and sanitation among students. Concepts on aquatic ecosystems, the impact of climate change on water resources, the adverse effects of water pollution, and water pollution prevention laws are dealt in curriculum. Research activities focused on SDG 6 has published 18 articles during the year 2023.

Green Rooftop:
Rainwater col lected at Nitte University is thoughtfully harvested and stored for the specific purpose of nurturing the greenery on roof terrace. Eco-friendly approach adopted conserves water and endorsed hallmark initiative towards sustainable campus practices, ensuring environmental impact remains minimal while promoting lush and vibrant green spaces.

Outreach programs:
- Nitte university conducted sessions to sensitize 7500 school children towards a sustainable future, emphasizing the importance of water conservation on 11 February 2023.
- Nitte university in collaboration with Dr. M Ramanna Shetty Memorial English Medium High School launched Nitte Climate Action Programme (NCAP) on 26th October 2023 at the school. NCAP aims to raise awareness about climate change and sustainable practices, inspiring young minds to think innovatively and emphasizing the importance of principles of reduce, reuse, and recycle.
- NUCSER adopted the Someshwar
Temple lake at Ullal, Mangaluru,
organizing an event on 16th
December 2023 to clean the lake and
its surroundings, removing weed
plants, plastic waste, and other
debris, and raising awareness about
water body conservation.


| Nitte (DU) incorporates stringent water conservation measures into its building design and construction processes, ensuring compliance with the National Building Code of India 2016 (NBC 2016) and standards IS1172 and IS2064. The institution also adheres to the Environmental Guidelines for Buildings by the Ministry of Environment, Forests & Climate Change, Government of India. |

|

Key practices include:
- Innovative Water Retention Techniques: Using water-retaining materials like cloth / gunny bags during curing processes and "ponding" on flat concrete structures to minimize water consumption.
- Adoption of curing chemicals and techniques that reduce water requirements.
- Installation of water-efficient fixtures such as push-cock taps, sensor- based taps, aerators, pressure inhibitors, and flow regulators.
- Provision of separate pipelines for potable water, recycled water, and treated water.
- Open wells and natural water bodies are used for rainwater harvesting, prioritizing sustainable water sources over borewells.
- Collaboration with external landowners for rainwater use from nearby storage ponds, supported by formal Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs).
- Collaboration with external landowners for rainwater use from nearby storage ponds, supported by formal Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs).
- Board rooms are equipped with water filters and dispensers to avoid bottled water.
Integration in Curriculum:
Nitte (DU) also incorporates Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6) principles into various educational programs to foster a deep understanding of water conservation and sanitation among students. First-year MBBS students receive early clinical exposure on solid waste and sewage disposal at the household level. Various courses, including MBBS, MD/MS, MSc Nursing, BSc Nursing, BSc Biomedical Sciences, BSc Medical Imaging and Technology, BSc Anesthesiology and Operation Theatre Technology, BSc Medical Laboratory Technology, and Bachelor of Architecture, include curricula addressing the importance of aquatic ecosystems, the impact of climate change on water resources, the adverse effects of water pollution, and relevant water pollution prevention laws.
Supporting Water Conservation Projects and Innovations
1. Biosorption Technology for Cadmium Removal:
Nitte (DU) has developed a ground breaking technology for removing cadmium from contaminated water using non-living, microparticular biomass. This eco-friendly method shows promise for commercial applications in water filters and purifiers, contributing to sustainable water purification systems.
https://dstnutec.in/user/eventInfo/120
2. Water Quality Assessment Using FAHP:
The university has patented a method for water quality assessment of river basins using the Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchy Process (FAHP). This decision support system evaluates water quality based on criteria such as domestic, irrigation, aquatic life, industrial, and recreational uses, aiding in prioritizing and selecting sites for water quality management interventions.
3. Communiy-Led River Rejuvenation Projects:
- Vrishabhavathi River Rejuvenation: A project by Ms. Kavya Amin from Nitte Institute of Architecture focuses on rejuvenating the Vrishabhavathi river in Bengaluru's Malleshwaram neighborhood, proposing green buffer zones along the canal edge to enhance the ecosystem and community engagement.
- Sulthan Battery Rejuvenation: A project by Mr. Harikiran, Ms. Shahana, and Ms. Nabeela addresses the rejuvenation of Sulthan Battery and its surrounding context in Mangalore, aiming to reconnect the community with the river through improved accessibility, sanitation, and infrastructure.
Patent filed:
Aqua-Hydroponic Integrated with Interlocking Clay Brick Building for Vegetation Cultivation



.png)
